|
Note: Click on images to increase size.
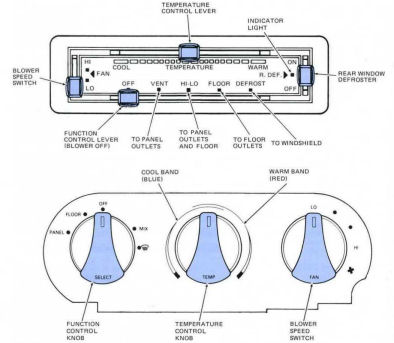 Air conditioning (A/C) means controlling the temperature, humidity, and quality of the air
inside the car.
These objects are achieved by (1) ventilation, (2) cooling (refrigeration) and dehumidifying, and (3) heating systems.
Adjustments are made at the Instrument Panel (Dashboard).
Air conditioning (A/C) means controlling the temperature, humidity, and quality of the air
inside the car.
These objects are achieved by (1) ventilation, (2) cooling (refrigeration) and dehumidifying, and (3) heating systems.
Adjustments are made at the Instrument Panel (Dashboard).
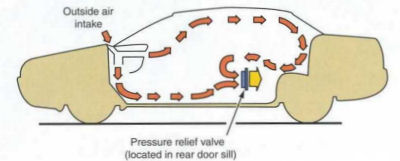 Ventilation carries fresh air into the car to replace stale air. Opening windows is the simplest
way to obtain fresh air. A blower motor and fan forces additional air into the car.
Ventilation carries fresh air into the car to replace stale air. Opening windows is the simplest
way to obtain fresh air. A blower motor and fan forces additional air into the car.
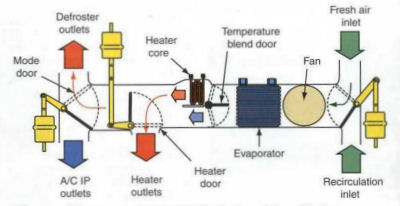 Heating the air inside the car is provided by the heat from the engine cooling water. It
circulates through the heater core to heat the air passing through it. In the diagram, fresh air (right top) is pushed by
a fan through the heater core and then exits to the car vents located in various places, including the defroster outlet at the
bottom of the windshield.
Heating the air inside the car is provided by the heat from the engine cooling water. It
circulates through the heater core to heat the air passing through it. In the diagram, fresh air (right top) is pushed by
a fan through the heater core and then exits to the car vents located in various places, including the defroster outlet at the
bottom of the windshield.
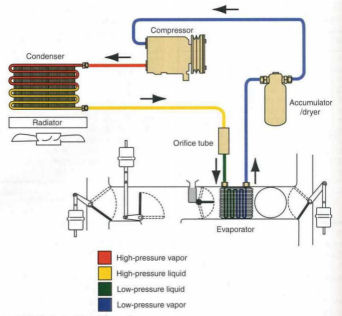 Cooling the air inside the car is provided by a confined gas that cools air and dehumidifies the car air.
(See diagram.) The principle involved is that as the refrigerant changes from a liquid to a gas, heat is absorbed.
This heat is extracted from the air inside the car. The refrigerant leaves the compressor as a high-temperature,
high-pressure vapor. It passes through the condenser located in front of the cooling radiator, where the incoming
atmospheric air absorbs the heat of the refrigerant to condense it into a high-temperature, high-pressure liquid.
Then it flows into the evaporator where it absorbs heat from the car air, thus warming so that it vaporizes into a
low-temperature, low-pressure vapor while cooling the evaporator and the car air
forced through it by a blower. It is cleaned and dehumidified in the accumulator/dryer and stored there until it is needed.
The accumulator traps any liquid refrigerant traveling with the vapor. The accumulator also contains a
dessicant, a drying substance, that adsorbs that removes water vapor (moisture) from the refrigerant.
The refrigerant is then conveyed back to the compressor as a cold, low pressure vapor for recycling.
Cooling the air inside the car is provided by a confined gas that cools air and dehumidifies the car air.
(See diagram.) The principle involved is that as the refrigerant changes from a liquid to a gas, heat is absorbed.
This heat is extracted from the air inside the car. The refrigerant leaves the compressor as a high-temperature,
high-pressure vapor. It passes through the condenser located in front of the cooling radiator, where the incoming
atmospheric air absorbs the heat of the refrigerant to condense it into a high-temperature, high-pressure liquid.
Then it flows into the evaporator where it absorbs heat from the car air, thus warming so that it vaporizes into a
low-temperature, low-pressure vapor while cooling the evaporator and the car air
forced through it by a blower. It is cleaned and dehumidified in the accumulator/dryer and stored there until it is needed.
The accumulator traps any liquid refrigerant traveling with the vapor. The accumulator also contains a
dessicant, a drying substance, that adsorbs that removes water vapor (moisture) from the refrigerant.
The refrigerant is then conveyed back to the compressor as a cold, low pressure vapor for recycling.
|










![[image of flower]](../../ima/flowXS_03.gif)
![[image of flower]](../../ima/flowXS_03.gif)




